Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) is basically a tumor that originates in the gastrointestinal tract of the human stomach. In 2021, approximately 4,000 to 6,000 people will be diagnosed with GIST in the United States. GIST has no known cause, but it is linked to a mutation in the expression of the KIT protein.
If the person is suffering from Stromal Tumors, then they will feel abdominal pain, vomiting, blood in the stool, fatigue, and a feeling that their stomach is full even if they eat a small amount. The top oncology hospital in Delhi, which provides cancer treatment, is the Oncoplus Hospital. A CT scan is the best way to diagnose GIST in the body.
Normally, targeted therapies are used to cure the genes and proteins that help the cancer cells grow. This therapy treatment is provided in advanced cases when the patient’s tumor cannot be removed or when they do not respond to chemotherapy. In this article, you will learn about targeted drug therapy, which is used to treat GIST.
What are the factors on which the treatment depends?
At Oncoplus Hospital, you will get the best oncologist in Delhi. The doctors first determine various factors before giving the treatment to the patient. Like, the size of the tumor, genetic makeup, location of the tumor, whether the tumor has spread or not, and whether the tumor has ruptured on its own or because of surgery.
Targeted Drug Therapy
The drugs prescribed by doctors to treat targeted therapy are:
- Imatinib:
This is the first drug that is used to treat people suffering from GIST. It targets both KIT and PDGFRA proteins and blocks the tumor cells’ growth. Normally, this drug is helpful in advanced stages when the GIST is not completely removed with surgery or if the tumor is large and hard to remove, so in that situation, Imatinib is used to shrink the tumor to make the surgery possible.
- Sunitinib:
This drug is given to a patient whose tumor has not been stopped with Imatinib or if the patient cannot continue to take Imatinib for a long time. In this situation, doctors prescribed them Sunitinib, which is best for advanced GIST. It targets the KIT gene and also helps in preventing blood vessel growth in tumor. But there are some side effects of this drug, such as high blood pressure, heart problems, increased bleeding, and also liver problems.
- Ripretinib:
When Imatinib and Sunitinib are not helpful for treating people, then Ripretinib is given to the patient in advanced cases of GIST. This drug helps to shrink and slow tumor growth. It also targets kinase proteins such as KIT and PDGFRA. But sometimes the patients face some side effects like headaches, vomiting, high blood pressure, etc.
For more information about the targeted therapy for treating advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors, you can visit the top oncology hospital in Delhi.
What is gall bladder cancer?
Gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ placed on the right side of the abdomen, a bit below the liver. Its normally an inch in width and three to four inches long. It stores a digestive fluid called bile that is formed in the liver, which helps in digesting the fats. It is a helpful organ but not an important one, people live normally after getting their gall bladder removed. Gall bladder cancer is a very uncommon cancer, which originates in the tissues of gall bladder and is often identified late as there are no signs and symptoms in the initial stages. The exact reasons for gall bladder cancer are not known, though there are several risk factors, which increases the risk of gall bladder cancers.
Studies state that people between forty-five to sixty-five years of age are at risk. It is more prevalent among women in India, and gallstones remains the most common risk factor for gallbladder cancer, family history of gallstones doubles risk of gall bladder cancer. Being overweight too increases the risk of many types of cancers, including gall bladder cancer. Diet with increased intake of proteins, fats and cholesterol and meals low in fibre, vegetables and fruits has been suggested as a risk factor for Gall Bladder Cancer. If people have one or more risk factors, this doesn’t mean that people will get gall bladder cancer for sure. Numerous people with no exposure to risk factors also get cancer.
There is no certain way of preventing gall bladder cancers. We cannot control the risk factors such as age, gender, ethnicity and hereditary abnormalities. But we can always take precautions and adopt healthy living to reduce the risk factors such as obesity, doctors recommend to eat healthy and exercise often.
Include cereals, whole grains, at least two and half cups of vegetables and fruits daily in meals, limit intake of processed foods and red meat. Consult a cancer specialist if you experience abdominal pain, many people with gall bladder cancer have an aching feeling on the upper right part of the belly and experience lump in the abdomen. Rarer symptoms of gall bladder cancer includes loss of appetite, fever, and weight loss.
If you or your dear ones have any of these symptoms, consult our Cancer specialist at Oncoplus Hospital, Defence Colony, New Delhi without delay so that the cause can be diagnosed and treated, in time. Experts opine that surgery can’t cure gallbladder cancer, which has spread in other areas of the body. Clinicians use treatments, which may relieve signs and symptoms of cancer and make you as contented as possible, other treatment options include Chemotherapy, Radiation therapy, and Clinical trials. Tele Consult with our expert doctors at Oncoplus Hospital, Defence Colony, New Delhi, write to us info@oncoplus.co.in or call us at +91 85889 09091 to book an appointment and learn more about Gallbladder Cancer treatment.
Gallbladder cancer develops in the gallbladder, a tiny organ located under the liver, behind the lower right ribs. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile, which helps digest fats. High risk factors for gallbladder cancer are obesity and medical conditions that end up affecting the gallbladder, for instance gallstones, cysts or polyps. Women are twice as likely to develop this type of cancer than men.
Gallbladder cancer is rather rare, but when it does occur, it is largely diagnosed in its advanced stages. Gallbladder cancer can also prove to be difficult to diagnose, in part because the gallbladder is rather small and buried deep within the body, making tumours much harder to find. Also, the symptoms will not typically appear until the cancer has reached an advanced stage.
At Oncoplus, South Delhi’s best cancer hospital, we deploy a range of diagnostics and techniques to better diagnose and stage all cancer treatment and tailor customised cancer treatment plans for our patients’ needs. We also provide support and counselling that may help you manage the side effects of your treatment, so you can better maintain your strength, stamina and keep the quality of life you want to: throughout treatment.
We target and treat gallbladder tumours with highly sophisticated, evidence-backed treatment and technology. A multidisciplinary team of gallbladder cancer experts will answer all your questions and recommend the best cancer treatment options based solely on your unique diagnosis and needs.
The Common courses of treatment for gallbladder cancer include:
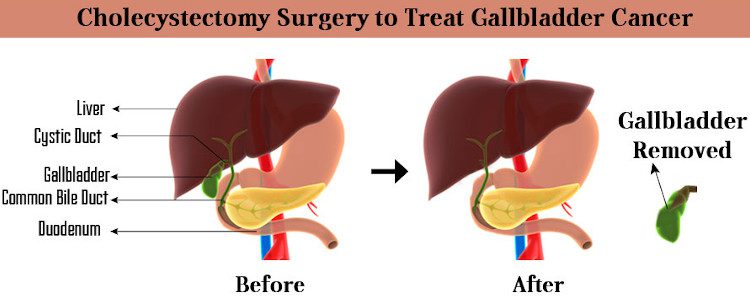
Surgery
Surgery is a common treatment for gallbladder cancer, and is used to remove the tumor or relieve symptoms. It may also be used to help alleviate pain if the cancer is more widespread.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used in addition to surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence or in cases where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Radiation therapy
Radiation may also be used after surgery or as a palliative treatment if the cancer has progressed.
Support and care
We understand managing the side effects of gallbladder cancer treatment is most critical to maintaining your quality of life. In addition to treating your cancer with evidence-based conventional approaches, our team will recommend various supportive care therapies designed to help you stay strong throughout treatment. They may include:
Nutritional support
Every patient has the option of meeting with a registered dietitian.
Pain management
Pain management is a branch of medicine focused on reducing pain and improving quality of life through an integrative approach to care.
Oncology rehabilitation
Oncology rehabilitation includes a wide range of therapies designed to help you build strength and endurance.