Pregnancy is a transformative and joyous experience for many women, but it can also present unique challenges when managing a chronic condition like Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). CLL is a type of blood cancer characterized by the abnormal proliferation of white blood cells, particularly lymphocytes. While CLL is more commonly diagnosed in older adults, it can also occur in younger individuals, including women of childbearing age. Navigating pregnancy with CLL requires careful consideration, specialized medical care, and close collaboration between healthcare providers to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Understanding Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
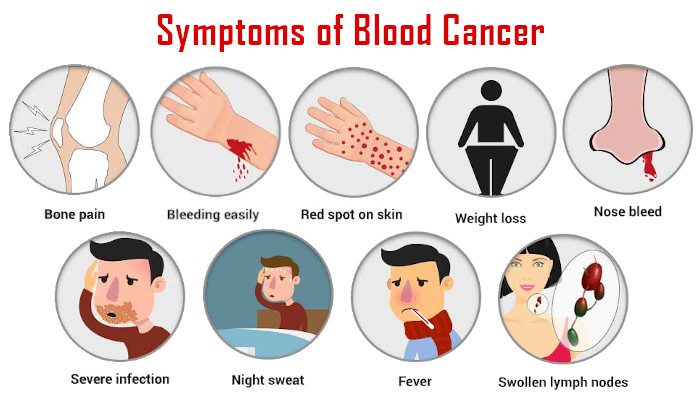
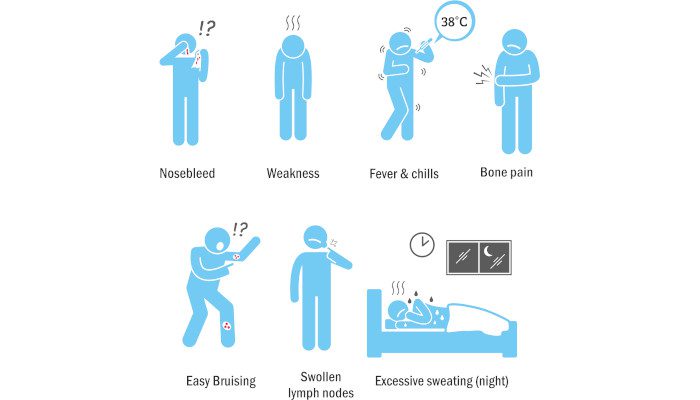
CLL is a chronic and slowly progressing cancer that primarily affects the immune system. It is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal lymphocytes in the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic tissues. The exact cause of CLL is not fully understood, but certain genetic and environmental factors may contribute to its development. Common symptoms of CLL include enlarged lymph nodes, fatigue, recurrent infections, and abnormal bleeding.
Impact of CLL on Pregnancy
Managing CLL during pregnancy poses unique challenges due to the complex interaction between maternal health, cancer progression, and fetal development. The hormonal changes associated with pregnancy can influence the behavior of CLL cells, potentially affecting disease progression. Additionally, the treatment options for CLL must be carefully evaluated to minimize risks to the developing fetus.
Key Considerations for Pregnancy with CLL
- Pre-Pregnancy Counseling: Women diagnosed with CLL who are considering pregnancy should seek pre-conception counseling from a hematologist or oncologist specializing in CLL. This consultation is essential for discussing fertility preservation options, assessing disease activity, and evaluating the potential risks and benefits of pregnancy.
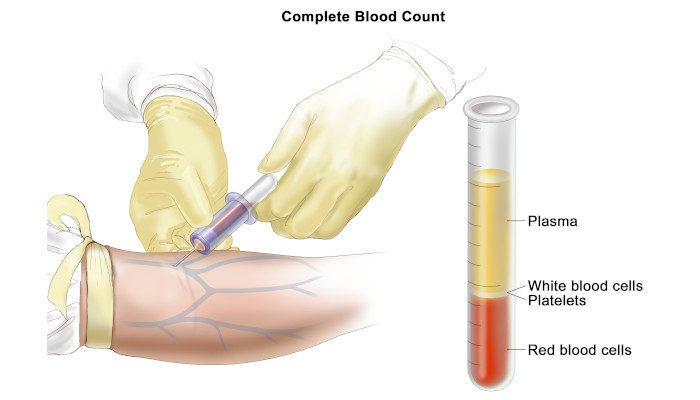
- Disease Monitoring: Regular monitoring of CLL during pregnancy is critical to assess disease progression and detect any complications. Blood tests, imaging studies, and consultations with hematologists will help guide treatment decisions and ensure optimal maternal and fetal outcomes.
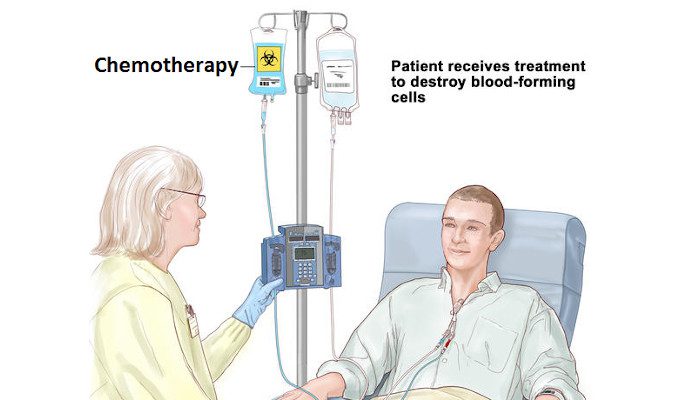
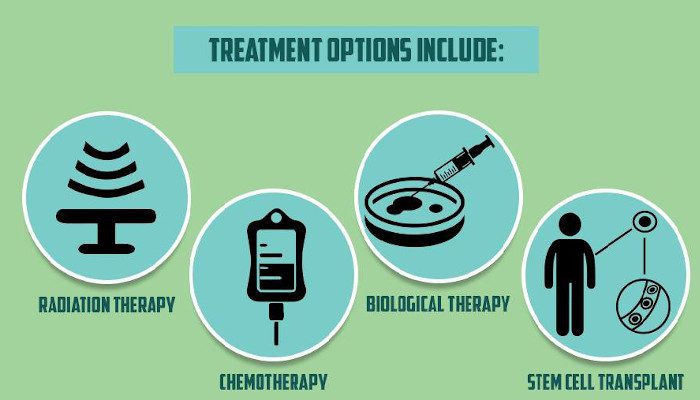
- Treatment Decisions: The management of CLL during pregnancy requires a multidisciplinary approach involving oncologists, hematologists, obstetricians, and maternal-fetal medicine specialists. Treatment options such as chemotherapy and targeted therapies may be deferred or modified to minimize fetal exposure while maintaining maternal health.
Managing Pregnancy with CLL: Practical Tips
- Open Communication: Maintain open and honest communication with your healthcare team about your CLL diagnosis and pregnancy plans.
- Prenatal Care: Attend all prenatal appointments and recommended CLL monitoring visits to ensure comprehensive care.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopt a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate rest to support overall well-being during pregnancy.
- Genetic Counseling: Consider genetic counseling to assess the risk of passing CLL to your child and explore family planning options.
Finding the Best Cancer Doctor in Delhi Identifying the best medical care for managing CLL during pregnancy is essential for ensuring optimal outcomes. Here are steps to find top cancer doctors and hospitals in Delhi:
- Research and Recommendations: Seek referrals from trusted sources, including primary care physicians, hematologists, or patient advocacy groups specializing in blood cancers.
- Hospital Reputation: Look for hospitals with a strong reputation for oncology care, including expertise in blood cancer treatment in Delhi and maternity services. Consider factors such as medical expertise, facilities, patient reviews, and success rates.
- Consultation and Second Opinions: Schedule consultations with recommended oncologists to discuss treatment options, pregnancy management, and postpartum care. Don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion to make informed decisions about your care.
Conclusion
Managing pregnancy with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia requires careful planning, specialized medical care, and ongoing monitoring. By working closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, women with CLL can navigate pregnancy safely while prioritizing their health and the well-being of their baby. It’s essential to stay informed about treatment options, communicate openly with healthcare providers, and seek support from loved ones throughout the journey. With proper management and guidance, women with CLL can have successful pregnancies and healthy outcomes.
Did you know that cancer claims thousands of lives worldwide each year? However, early cancer detection is thought to increase the likelihood of a complete and successful recovery. Thus, you require a highly skilled team of cancer specialists and state-of-the-art technology for an early diagnosis. Blood cancer is one of the forms of cancer that affects people around the world as it attacks your blood cells. Myeloma, lymphoma, and leukemia are the three most prevalent forms of blood cancer. Discovering the top blood cancer hospital in Delhi is a journey characterized by the pursuit of excellence, compassion, and cutting-edge medical care in the complex world of healthcare. The significance of a specialized cancer hospital in Delhi cannot be emphasized, as people dealing with blood cancer seek comfort and efficient treatment. With the all-inclusive guide in this blog post, we are here to examine the key features that distinguish the top blood cancer research institutes in the busy metropolis of Delhi.
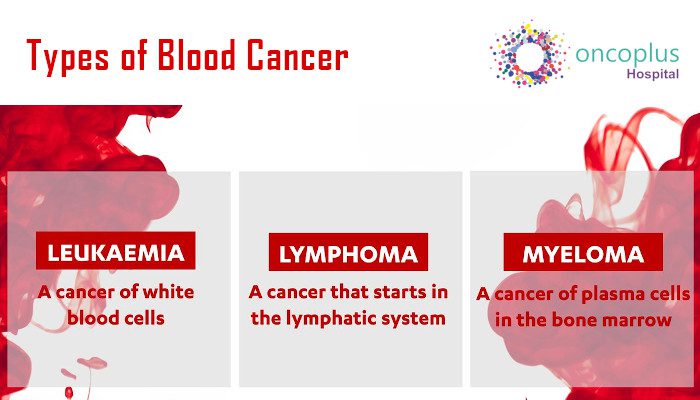
Understanding Blood Cancer:
It is essential to understand the complications of blood cancer before stepping into the world of healthcare facilities. Hematologic cancer, another name for blood cancer, is the collective term for a class of cancers that impact the lymphatic, bone marrow, and blood systems. These include myeloma, lymphoma, and leukemia, each of which calls for a different strategy for diagnosis, care, and treatment.
Read More Blog: Blood Cancer – Keep Calm And Fight On
Entire Diagnostic Capabilities:
Its extensive diagnostic capabilities are among the best blood cancer hospitals in Delhi’s distinguishing features. With cutting-edge laboratory services and sophisticated imaging methods, the hospital does everything possible to guarantee precise and prompt diagnoses. Blood cancer must be detected early to be effectively managed, and the hospital’s dedication to accurate diagnostics is essential to enhancing patient outcomes.
Cutting-Edge Methods of Treatment:
Combining traditional and cutting-edge treatment modalities is essential in the fight against blood cancer. The top blood cancer hospital in Delhi is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment. It provides a range of treatments, such as immunotherapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, and targeted therapies. With these modalities, patients have the best chance of recovery because they are specifically designed to fit the type and stage of blood cancer.
Professional Oncology Group:
An outstanding cancer hospital in Delhi would have its oncology team at its core. A team of highly qualified and experienced hematologists, oncologists, and support personnel are assembled by the best hospital for blood cancer, and they collaborate to create individualized treatment plans for each patient. Thanks to this multidisciplinary approach, patients will receive the most thorough and efficient care throughout their journey.
Advanced Techniques of Treatment:
The fight against blood cancer frequently necessitates combining conventional and cutting-edge therapeutic approaches. The top blood cancer hospital in Delhi is furnished with state-of-the-art equipment. It provides a range of treatments, such as immunotherapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, and targeted therapies. With these modalities, patients have the best chance of recovery because they are specifically designed for their type and stage of blood cancer.
Patient-Centric Approach:
The best blood cancer hospital in Delhi strongly emphasizes a patient-centric approach in addition to medical expertise. A caring and encouraging atmosphere is essential for navigating the emotional and physical difficulties associated with blood cancer. The hospital ensures patients and their families get the essential direction and emotional support throughout their journey by providing resources like support groups and committed patient counselors.
Research and Innovation:
Delhi’s top blood cancer hospital actively pursues research and innovation as part of its commitment to excellence. Its participation in clinical trials facilitated the hospital’s ability to offer patients the newest and most effective treatments, collaborations with research institutions, and commitment to staying at the forefront of medical innovation.
Effects of Delhi’s Cancer Hospital:
The influence of Delhi’s best hospital for blood cancer goes well beyond its boundaries. Through its provision of excellent care, promotion of research, and advancement of medical science, this institution has a significant impact on cancer treatment, not only in Delhi but around the nation. The hospital’s influence reaches into communities, igniting hope and resilience in blood cancer patients.
In summary, a big step towards conquering the difficulties this complicated illness presents is identifying the top blood cancer hospital in Delhi among the confusing array of healthcare alternatives. So, if you’re looking for the best blood cancer hospital, then you should consult with the hospital in Delhi. Delhi is a center for cutting-edge healthcare and home to a number of esteemed oncology-focused institutions. However, one hospital stands out when it comes to providing the specialized care needed for blood cancer patients: Oncoplus. The combination of knowledge, innovation, and empathy in the battle against blood cancer is demonstrated by the best hospital for blood cancer in Delhi, just like Oncoplus. The hospital is renowned for its unwavering dedication to excellence, and offers patients with blood cancer comprehensive care by fusing state-of-the-art technology, a multidisciplinary approach, and a compassionate ethos. Oncoplus provides not only medical care but also hope, support and commitment to a future free from the shadow of blood cancer, serving as a beacon of hope for individuals and families as they navigate diagnosis, treatment and let’s move forward on the path to recovery.
India witnesses’ approximately 1,200.000 new cancer cases each year, according to the latest projections that people will develop some form of cancer during their lifetime.
What is cancer?
According to the NCI: cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells. Normally, human cells grow and multiply to form new cells as the body needs them. When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
Sometimes this orderly process breaks down, and abnormal or damaged cells grow and multiply when they shouldn’t. These cells may form tumors, which are lumps of tissue. Tumors can be cancerous or not cancerous (benign).
Cancerous tumors spread into, or invade, nearby tissues and can travel to distant places in the body to form new tumors (a process called metastasis).
Cancerous tumors may also be called malignant tumors. Many cancers form solid tumors, but cancers of the body, such as leukemia, generally do not.
Benign tumors do not spread into or invade nearby tissues; when removed, benign tumors usually don’t grow back, whereas cancerous tumors sometimes do. Benign tumors can sometimes be quite large, however, and some can cause serious symptoms or be life-threatening, such as benign tumors in the brain.
Differences between cancer cells and normal cells: Grow in the absence of signals telling them to grow. Normal cells only grow when they receive such signals.
* Ignore signals that normally tell cells to stop dividing or to die.
* Hide from the immune system. The immune system normally eliminates damaged or abnormal cells.
Many times, cancer cells rely so heavily on these abnormal behaviors that they can’t survive without them.
For example, some cancer therapies prevent blood vessels from growing toward tumors, essentially starving the tumor of needed nutrients.
How does cancer develop?
Cancer is a genetic disease that is caused by changes to genes that control the way our cells function, especially how they grow and divide.
* Genetic changes that cause cancer can happen because of errors that occur as cells divide.
* They were inherited from our parents.
* DNA damage is caused by harmful substances in the environment, such as the chemicals in tobacco smoke and ultraviolet rays from the sun.
The body normally eliminates cells with damaged DNA before they turn cancerous; each person with cancer treatment has a unique combination of genetic changes. As the cancer continues to grow, additional changes will occur. Even within the same tumor, different cells may have different genetic changes.
Types of Genes That Cause Cancer:
The genetic changes that contribute to cancer tend to affect three main types of genes: proto-oncogenes.
Tumor suppressor genes and DNA repair genes—these changes are sometimes called drivers of cancer.
Proto-oncogenes are involved in normal cell growth and division. However, when these genes are altered in certain ways or are more active than normal, they may become cancer genes, allowing cells to grow and survive when they should not.
Tumor suppressor genes are also involved in controlling cell growth and division; cells with certain alterations in tumor suppressor genes may divide in an uncontrolled manner.
DNA repair genes are involved in fixing damaged DNA. Cells with mutations in these genes tend to develop additional mutations in other genes and changes in their chromosomes.
Such as duplications and detection of chromosome parts, together these mutations may cause the cells to become cancerous.
When cancer spreads:
Cancer that has spread from the place where it first formed to another place in the body is called metastatic cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
Tissue changes that are not cancer:
Not every change in the body’s tissues is cancer. Some tissue changes may develop into cancer if they are not treated, however. Here are some examples of tissue changes that are not cancer but, in some cases, are monitored because they could become cancer:
1: HYPERPLASIA: This occurs when cells within a tissue multiply faster than normal and extra cells build up.
2: DYSPLASIA: This is a more advanced condition than hyperplasia.
3: CARCINOMA IN SITU: In an even greater way, although it is sometimes called stage 0 cancer because the abnormal cells do not advance the condition,.
They invade nearby tissue the way that cancer cells do, but because some carcinomas in situ may become cancer, they are usually treated.
Read More: Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) Of Your Breast
Types of cancer:
There are more than 100 types of cancer. Types of cancer are usually named for the organs or tissues where they form, for example.
Lung cancer starts in the lungs and brain; cancer may also be described by the type of cells that formed them, such as epithelial cells or squamous cells.
1: CARCINOMA: Carcinomas are the most common type of cancer. They are formed by epithelial cells, which are the cells that cover the inside and outside surfaces of the body.
2: SARCOMA: Sarcomas are cancers that form in bone and soft tissues, including muscle, fat, blood vessels, lymph vessels, and fibrous tissue such as tendons and ligaments.
3: LEUKEMIA: Cancer that begins in the blood-forming tissue of the bone marrow is called leukemia. There are four common types of leukemia, which are grouped based on how quickly the disease is worse (acute or chronic) and on the type of blood cell the cancer starts in (lymphoblastic or myeloid). Acute forms of leukemia grow quickly, and chronic forms grow more slowly.
4: LYMPHOMA: Lymphoma is a cancer that begins in lymphocytes (T cells or B cells). These are the fighting white blood cells that are part of the immune system. In lymphoma, abnormal lymphocytes build up in lymph nodes and lymph vessels, as well as in other organs of the body.
Read More Blog: Blood Cancer – Keep Calm and Fight On
The main two types of lymphoma are:
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA: People with this disease have abnormal lymphocytes that are called Reed-Sternberg cells; these cells usually form from B cells.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: This is a large group of cancers that starts in lymphocytes. The cancer can grow quickly or slowly and can form from B cells or T cells.
Multiple Myeloma: Multiple myeloma is cancer that begins in plasma cells, another type of immune cell. abnormal plasma cells, another type of immune cell; the abnormal plasma cells are called myeloma cells; multiple myeloma is also called plasma cell myeloma; and Kahler disease.
Melanoma is a cancer that begins in cells that become melanocytes, which are specialized cells that make melanin (the pigment that gives skin its color). Most melanomas form on the skin, but melanomas can also form in other pigmented tissues, such as the eye.
Brain and spinal cord tumors
There are different types of brain and spinal cord tumors. These tumors are named based on the type of cell in which they formed and where the tumor first formed in the central nervous system. For example, an astrocytic tumor begins in star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes, which help keep nerve cells healthy. Brain tumors can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
Read More Blog: Brain Stroke: Warning Signs, Symptoms, and Prevention
Other types of tumors
Germ cell tumors
Germ cell tumors are a type of tumor that begins in the cells that give rise to sperm or eggs. These tumors can occur almost anywhere in the body and can be either benign or malignant.
Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors form from cells that release hormones into the blood in response to a signal from the nervous system. These tumors, which may produce higher-than-normal amounts of hormones, can cause many different symptoms. Neuroendocrine tumors may be benign or malignant.
Carcinoid Tumors
Carcinoid tumors are a type of neuroendocrine tumor. They are slow-growing tumors that are usually found in the gastrointestinal system (most often in the rectum and small intestine). Carcinoid tumors may spread to the liver or other sites in the body, and they may secrete substances such as serotonin or prostaglandins, causing carcinoid syndrome.
Symptoms and Causes of Anemia Caused by Iron Deficiency:
Anemia is caused when your blood does not have an adequate amount of healthy red blood cells, which provide oxygen to the body’s tissues. In this situation, it is natural that your body has weakness, is short of breath, and feels tired all the time. This is the common type of anemia that occurs due to the iron deficiency that your body requires to make hemoglobin. Iron supplements are available on the market to cure anemia. But if the patient has internal bleeding, then doctors recommend that they undergo further testing or treatment.
There are many people who do not know that they are suffering from iron-deficiency anemia. Generally, women suffer more from iron deficiency, as there is a loss of iron in the blood due to heavy menstruation or during pregnancy. Not only this, but a poor diet or intestinal diseases also lead to iron-deficiency anemia. In this blog, you will read about the symptoms and causes of anemia caused by iron deficiency.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia:
The symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia are general fatigue, pale skin, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, cravings to eat items that have no nutritional value, swelling in the tongue, headache, brittle nails, cold hands and feet, dizziness, and an irregular heartbeat.
The Main Causes of Iron Deficiency Anemia
The main causes of iron-deficiency anemia are as follows:
- Blood loss due to menstruation:
If girls have heavy menstrual bleeding, then due to the excess of blood loss, they suffer from iron-deficiency anemia. And in the case of pregnancy, women’s bodies require more iron in order to create sufficient oxygen for the baby. During pregnancy, mother and child both require blood for proper oxygen.
- Inadequate Iron Intake:
A deficiency of iron occurs in your body when you eat a small amount of iron over a long period of time. It is recommended to consume nutritious foods that are high in iron, like meat, eggs, and green leafy vegetables. Pregnant women and young children require more iron-rich foods in their diets because iron is essential for the growth and development of the body.
- Genetic Issue:
There are some diseases, such as celiac disease, that run in families and make it difficult to absorb sufficient iron. The issue occurs due to genetic disorders or mutations. This type of genetic disorder prevents your intestines from absorbing iron. Other genetic disorders can also result in anemia.
- Internal bleeding:
Internal bleeding can also occur from medical disorders, which can result in iron-deficiency anemia. Examples of internal bleeding are colon cancer, stomach ulcers, and polyps in the colon or intestines. All types of cancer treatment are available in Delhi. Not only this, but regular use of painkillers like aspirin can lead to stomach bleeding.
- inability to absorb iron
The ability to absorb iron in your body can also be affected by intestinal conditions or surgeries. Even if you consume an adequate amount of iron in your diet, diseases like celiac disease or gastric bypass surgery will reduce the amount of iron in your body.
How to Diagnose Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Iron-deficiency Anemia can be diagnosed with a complete medical history and physical examination. Doctors recommend an iron deficiency check-up when there are problems in your body like complaints of tiredness, abnormal paleness, a fast heartbeat, etc. The medical examination of iron deficiency is through a blood test that measures the amount of hemoglobin present in your body, which will measure the amount of iron present in the blood. Other tests for iron deficiency are bone marrow aspiration or biopsy, and upper or lower endoscopy.
Treatment for iron-deficiency anemia can be determined by the doctor according to your age, health, and medical history. Eat an iron-rich diet like meat, chicken, fish, broccoli, whole-wheat bread, etc. to raise the iron level in the blood. It is suggested that, before taking an iron supplement, always consult your doctor for your daily iron requirement.
Leukemias are cancers that begin in cells that normally develop into various types of blood cells. Most leukemias begin in the early stages of white blood cells, but some leukemias begin in other types of blood cells.
Acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL) is a type of leukaemia that is also known as acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. The term “acute” refers to the fact that the leukaemia can progress quickly and, if left untreated, will most likely be fatal within a few months. The term “lymphocytic” refers to the fact that it develops from early (immature) forms of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.
Everything begins in the bone marrow (the soft inner part of certain bones, where new blood cells are made). Most of the time, leukaemia cells infiltrate the bloodstream quickly.
LEUKEMIA TREATMENT IN INDIA
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (chemo) is the application of drugs to the treatment of cancer. Chemotherapeutic drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy is therefore useful for cancers that have spread throughout the body, such as leukaemia.
- Targeted Therapy
Drugs used in targeted therapy work by attacking specific parts of cancer cells. They are not the same as standard chemotherapy (chemo) drugs. They occasionally work when chemo does not, and they frequently have different side effects. Some of these medications may be beneficial in certain cases of acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL).
- Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is the use of medications to assist a patient’s immune system in more effectively recognising and destroying cancer cells. Certain types of immunotherapies are now being used to treat acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL).
- Surgery
In the treatment of ALL, surgery plays a very limited role. Because leukaemia cells spread so widely throughout the bone marrow and blood, surgery cannot cure this type of cancer. Surgery, with the exception of a possible lymph node biopsy, is rarely used in the diagnosis of ALL, as this is typically done with a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
- Radiation therapy:
Radiation treatment is similar to getting an x-ray, except that the radiation is much stronger. The procedure is completely painless. Each treatment is only a few minutes long, but the setup time in getting you into position for treatment – is usually longer. The number of treatments you receive is determined by the reason radiation therapy is used.
- Stem Cell Transplant
A stem cell transplant (SCT) allows doctors to use higher doses of chemotherapy (sometimes with radiation) to kill cancer cells. Following the completion of these treatments, the patient receives an infusion of blood-forming stem cells to restore their bone marrow.
- Typical Treatment
Treatment is usually divided into three stages:
- Incorporation (remission induction): The purpose of induction chemotherapy is to put the leukaemia into remission (complete remission).
- Reorganization (intensification): The next phase usually consists of another relatively short course of chemo with many of the same drugs used for induction therapy.
- Maintenance: Following consolidation, the patient is usually started on a methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine maintenance chemotherapy regimen (6-MP).
Diarrhoea antibiotic shows potential in treating aggressive blood cancer
A form of aggressive blood cancer might be found to be more sensitive to chemotherapy with the use of an antibiotic currently available for treating diarrhoea, as per novel research published in Science Translational Medicine. The study was funded by Cancer Research UK and Blood Cancer UK, the study looked to tackle a certain type of acute myeloid leukaemia of which contains a genetic modification called MLL, thorough investigations on cancer’s origins.
This form of leukaemia, often called MLL-AML, has a peculiarly poor prognosis as it suddenly turns resistant to standard chemotherapies. Resolving this resistance had proven to be a major challenge in treating this cancer, and has left patients with no other alternative.
Even the best cancer doctors in Delhi concur on the fact that resistance to treatments is the biggest challenge cancer research faces and coming to terms with the fact that there is no other treatment available is undeniably the worst thing a doctor wants to tell their patient. These recent findings demonstrate how unravelling the biology of cancer has lead to new discoveries, and how we could already have a huge array of drugs out there that could help boost the effects of current treatments.
What is MLL-AML?
Acute myeloid leukaemia is a variegated disease, with different sub-types dependent on the genetic mutations that are causing it. This affects how successfully the cancer is treated, with some sub-types having a far poorer prognosis than others. MLL-AML is deadly, with only 1 in 4 patients surviving for 2 to 5 years or so.
The researchers observed how MLL-AML developed in humans for the first time, through establishing a new way of modelling how the stem cells that make our blood could turn into AML when altered by the MLL genetic alteration.
It’s a significant moment for cancer treatment across the world.
After the research that threw light on the origins of MLL leukaemia in mice almost 18 years ago, this development is an important milestone for AML research and provides a new way for screening and identifying new targets to treat.
Using this new approach, the team found that the disease could actually originate from 2 different types of cells, with one causing more resistant disease than the other.
Studying the more resistant type in detail revealed it produced way more of a particular protein – ABCC3 – than the other one, and this could be responsible for making it more resistant to chemotherapy.
When this theory was confirmed in human cells: the team got rid of the cell’s ability to produce any more ABCC3, and it was far more sensitive to chemotherapy.
The next step forward was finding a drug that could stop ABCC3 from being produced or prevent it from working at all. By researching, the team found a paper that showed fidaxomicin – an antibiotic prescribed to treat diarrhoea caused by the bacteria C. difficile – was rather effective for inhibiting ABCC3.
This was unexpected and, actually fortuitous, that there was a recent study showing an already approved antibiotic could work for this research. Testing the drug for the treatment of resistant MLL-AML, the team found it successfully sensitised cancer to chemotherapy in both the cells grown in the lab and in mice.
This is hugely promising and now we need to do further studies and testing with this approach in people with AML and see how many benefits it brings.