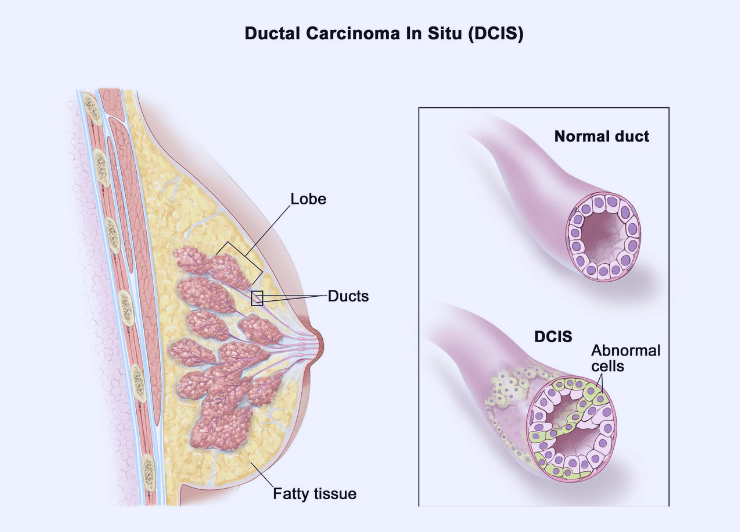
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the first form of breast cancer. It occurs when the abnormal cells present themselves inside a milk duct in the breast. Generally, these cells are non-invasive, meaning they do not spread out of the breast, but if left untreated, some DCIS cells can become invasive breast cancer that can spread. DCIS is frequently found during a mammogram for breast cancer screening. DCIS is also known as stage 0 breast cancer or intraductal carcinoma. DCIS is treatable, and the treatment options that are available for a woman are simple mastectomy and breast-conserving surgery (BCS). In this blog, you will read about the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment of DICS.
Read More Blog: A Guide On Breast Cancer
Symptoms of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS):
Generally, there are no specific symptoms of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). In the majority of cases, DICS is diagnosed through mammography, and it appears as a new calcium deposit and sometimes distortion of the breast tissue. But in a few cases, the symptoms are as follows:
- Itchy skin.
- Breast lump.
- Nipple discharges (like blood) are found.
Causes of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS):
The reason for ductal carcinoma in situ is not clear. But it normally forms when the DNA of breast duct cells experiences genetic mutations. The cells appear abnormal when the genetic mutations occur, but they do not spread out of the milk duct. The major factors that contribute to DCIS are your living environment, the genes passed down from your parents, and your lifestyle.
Risk factors for DCIS:
The risk factors for ductal carcinoma in situ (DICS) are as follows:
- Having a first child after 30 years of age
- If menopause begins after the age of 55,
- You will never be pregnant in your life.
- Background history of breast cancer in the family.
- having a menstrual period before the age of 12
- If you have a family history of breast cancer, such as atypical hyperplasia,
- If you have previously received radiation therapy to your breasts or chest,
- If you have dense breast tissue,
- Growing age is also a risk factor for DICS.
- If you have a genetic mutation, this also raises your risk of breast cancer.
DICS Grade:
Generally, the DICS grade tells the doctors how much the cell appears like normal breast cells. It helps your doctor determine the best course of treatment for you and how the DCIS may behave. The DCIS grade is divided into three grades: low grade, which slowly grows; intermediate grade; and high grade, which quickly grows in your breast. Normally, high-grade DCIS comes back after treatment and spreads into the other breast tissue.
Treatment Options for DICS
- Mastectomy:
If the area of DCIS is very large, then a simple mastectomy is needed. In this treatment, the entire breast is removed. This treatment is required when the breast contains multiple areas of DCIS or if BCS cannot entirely eradicate the DCIS, meaning cancer cells are still present in or near the surgical margins. Many doctors perform a SLNB (sentinel lymph node biopsy) in addition to a mastectomy as there are chances of finding invasive cancer. The majority of DCIS patients who undergo mastectomy do not require radiation therapy and may opt for immediate breast reconstruction.
- Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy):
In BCS, the doctor removes the tumor and also a small portion of healthy breast tissue that surrounds it. With BCS, lymph node removal is not required. After BCS, radiation therapy is performed. This lessens the possibility of cancer returning in the same breast. The women, who are at an early stage of DCIS, can choose between mastectomy and breast-conserving surgery (BCS).
- Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy is used to block hormones from reaching cancer cells. If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, this therapy is effective. It isn't a treatment for DCIS, but it is the therapy that is given after surgery or radiation in order to decrease the chances of developing DCIS. The treatment with tamoxifen for any woman or an aromatase inhibitor for women past menopause after the surgery can reduce the risk of DCIS or invasive cancer.
Read More Blog: Hormone Therapy For Prostate Cancer
The type of cancer that can be treated is ductal carcinoma in situ. The best cancer treatment in Delhi is available for patients. The available treatments for DISC will lower your chances of developing breast cancer. If you experience any side effects like breast swelling, breast soreness, skin irritation, etc., then immediately discuss them with your doctor.


Leave a Reply